News
The winter storm Xynthia seen by altimetry
The storm Xynthia crossed Western Europe on 26-28 February 2010. The combined effects of a strong atmospheric depression, high tides and strong winds caused extreme damages.
The storm Xynthia crossed Western Europe on 26-28 February 2010. It caused extreme damages mainly in France due to floods.
Wind speed and significant wave heigths measured by altimetry satellites on the storm path indicate a speed more near than 20 m/s off Vigo (Spain) and waves between 4.5 m and 6 m on 2010/02/27 8:30.
A strong atmospheric depression, as observed during Xynthia, creates hills at the sea surface. The situation is even worse when the effects of a strong atmospheric depression and high tides and strong winds are combined.
<link fileadmin images news mod_actus xynthia_wind_j1.png download>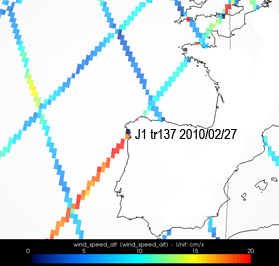 | <link fileadmin images news mod_actus xynthia_wind_en.png download>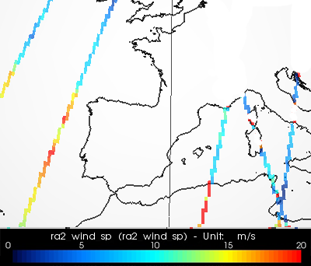 |
|---|---|
<link fileadmin images news mod_actus xynthia_swh_ku_j1.png download>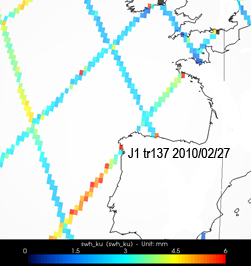 | <link fileadmin images news mod_actus xynthia_wind_j2.jpg download>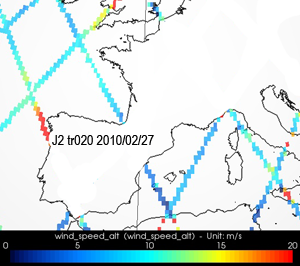 |
Maps of wind speed (in m/s) measured along-track by Jason-1 (top left), Envisat (top right) and Jason-2 (bottom right) on February 27, 2010, during the storm Xynthia.
Maps of significant wave heigths (in m) measured along-track by Jason-1 (top left) on February 27, 2010, during the storm Xynthia.
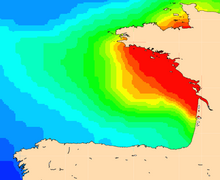
Maps of Mog2D (combining the effects of the atmospheric pressure, the wind meteorological forcing and the coastal intensification) show a sea level rising up to 85 cm on 2010/02/27 0:00 off Charente-Maritime and Vendée regions.
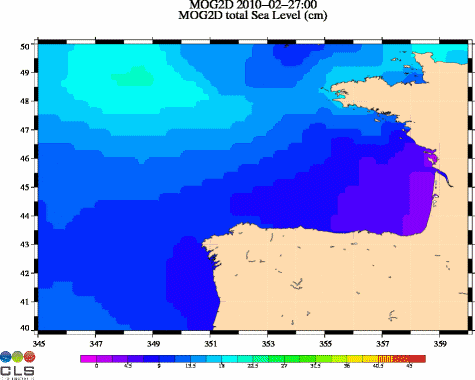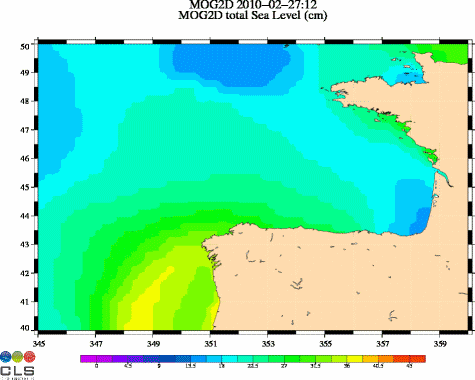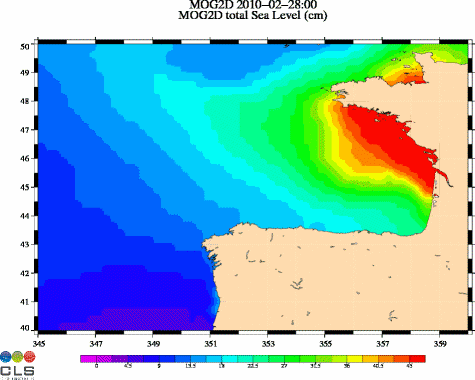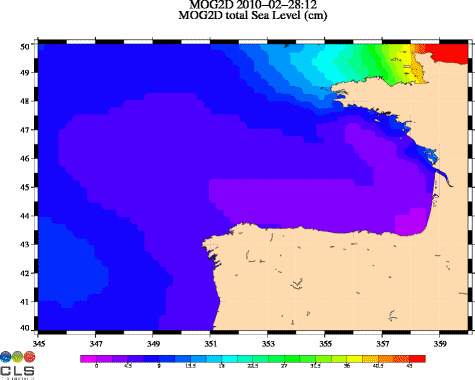
Ocean dynamic response (in cm, from 0 to 45 cm) due to atmospheric pressure and winds, from Mog2D model. (Credits CLS/Legos). See enlarged animation <link fileadmin images news mod_actus xynthia_mog2d_slev_21972_00_21973_12_big.gif download>here.