The Swot mission
Program




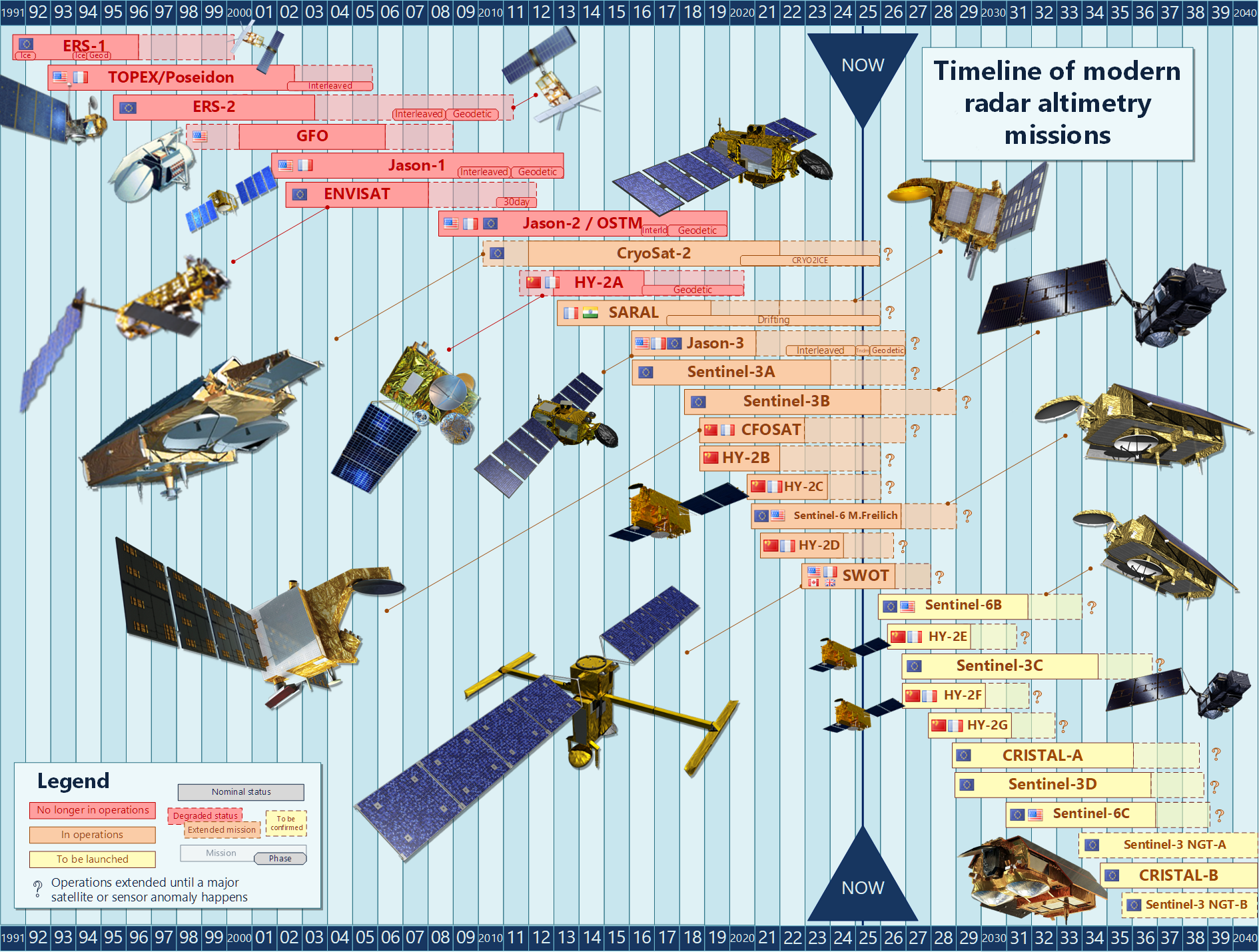
International partners have joined forces to develop the Swot mission: it is a major partnership between Nasa and Cnes, with a contribution from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA). Swot is the latest in a long line of missions accomplished in partnership between Cnes and Nasa. It started in 1992 with the launch of the Topex/Poseidon satellite and has been continuing through the series of Jason satellite missions since then.
Partners contribution
Nasa provides the payload module, the Ka-band Radar Interferometer (KaRIn), the radiometer, two location systems (a laser retroreflector array, a GPS receiver payload), ground support and launch services. Cnes provides the Swot spacecraft bus, KaRIn's Radio Frequency Unit (RFU), the dual frequency Ku/C-band Nadir Altimeter, the Doppler Orbitography and Radiopositioning Integrated by Satellite (DORIS) receiver package, satellite command and control. Both provide data processing infrastructure.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) contributes to KaRIn through a part of the high power amplification subsystem
The UK Space Agency (UKSA) contributes to a part of the RFU, ie the duplexer, which is a key component of KaRIn allowing the switching between emission and reception channels

Unprecedented funding
On March 2011, Swot has received funding from the PIA (Programme d’Investissements d’Avenir, Future Investments Programme). Cnes has included Swot mission in its program for Earth Observation Future, after recommendation by the Comité des Programmes Scientifiques (CPS).
On US side, the Swot mission is part of Nasa decadal plan for study of global change.
Working Group
To develop and implement this program, state, academic, and scientific partners organize themselves and meet together on a regular schedule. See Key dates.
The Swot Downstream Preparatory Program outlines the development of applications. Its topics are described here.
On scientific side, the Science Definition Team was a selected group of US/France/Canada/UK scientists who helped with defining the science goals and provide guidance and advice to the Swot project to ensure the mission meets its science requirements. Now the Science Working Team has taken over, selected upon periodic calls, and will continue on during the whole satellite's mission.